Norms and standards are a major dimension to take into account for quality assurance and industrial production. Do you need a quick reminder of the main regulations regarding your industrial activity? Find below the main quality assurance standards and industrial production norms to which you may be required to comply.
General Industries
Aerospace
Datacenters
Automotive
New energy vehicles
Quality assurance: Norms and standards you need to know
General norms and standards for Industry
ISO 9000: This international standard defines basic principles and terms for quality management systems. The standard describes the requirements to be met by the management of the company in order to comply with certain requirements in the implementation of quality management. It may be used both for the implementation of quality management within a company and to demonstrate to third parties that the company complies with certain requirements.
ISO 9001: This international standard defines the prerequisites to the quality management system in the event that an organization needs to demonstrate that its products conform to the requirements of customers and legislation and that it aims to improve customer satisfaction. The standard outlines a model for an entire quality management system and is central to organizations seeking ISO 9001 compliance.
IATF 16949: Requirements for Quality Management Systems. This specification describes special requirements for the application of ISO 9001 to vehicle and spare part production in the automotive industry. The previous version of this standard was known as ISO/TS 16949.

VDA 6.1 - 6.4: These codes of practice of the German automotive industry are binding on suppliers of German car manufacturers and are quite similar to the requirements of IATF 16949. The VDA 6 is classified into two areas, management and products & processes.
ISO/IEC 17025: This standard defines general requirements for the competence of measurement and calibration laboratories. ISO/IEC 17025 enables accredited laboratories to demonstrate that they generate valid measurement results, thereby promoting confidence in their work.
ISO 10012: This standard describes quality requirements for measurement management systems. The standard provides guidance for the effective management of measurement processes and metrological confirmation of measuring equipment and helps in ensuring that both measuring equipment and measurement processes are suitable for the intended purpose.
EURAMET cg-14: This is one of the most important torque calibration standards. It describes calibration procedures for torque measuring instruments. The results of the calibration process are classified and indicate the accuracy level of the measuring equipment. This standard is very similar to the German DIN 51309 upon which it is based.
VDI/VDE 2646: A German standard that defines the minimum requirements for the calibration of torque measuring equipment. It is often referred to as a factory standard as the procedure is considerably simpler than EURAMET cg-14. Contrary to EURAMET cg-14, the measurement results are not classified.
Discover our torque measurement systems

VDI/VDE 2645-2: This relatively new standard describes very comprehensive procedures for machine capability testing (MCT) on power tools used in tightening systems. This procedure uses different kinds of statistical analyses of the measured readings in order to provide an assessment of the tool’s performance. It covers only tools with a controllable target variable such as torque. Stall-type tools are not covered by this standard.
VDI/VDE 2647: This standard defines the procedure for tool type testing of power tools. The standard is very comprehensive and is used as a verification that a certain tool type is adequate for a particular production process.
VDI/VDE 2648: This standard defines procedures for the traceable calibration of rotational angle sensors and measuring equipment which measure the rotational angle either directly or indirectly via a gyroscope. This is currently the only verified calibration standard on the international market for angle calibration of transducers and is thus used as the basis for many national norms.
You want to know more about the calibration of transducers?

Discover our article: Precision tightening: Torque and angle, the essentials of industrial calibration
ISO 5393: specifies a performance test method for power assembly tools. This is the only international norm covering this subject and has recently been updated and extended to cover pneumatic as well as electric/battery-powered tightening systems. This norm does not recommend nor set any acceptance criteria.
ISO 6789: This norm defines the calibration procedure for torque wrenches, and is divided into two parts.
- Part 1: intended for manufacturers of the wrenches, describes mininum requirements for declaration of conformance.
- Part 2: intended for industrial users, describes requirements for calibration and determination of measurement uncertainty.
ISO 376: This standard describes the calibration procedure for force transducers, used for example in press systems in assembly processes. The calibration covers both tension and compression, and the standard has unified several national procedures into a single international reference.
VDI 2862: Although not a calibration standard, this norm describes the classification of joints using threaded fasteners and guides the selection of appropriate tools for each application. This has a strong impact on the type of calibration required for specific tools.
What is the Metrology Pyramid?
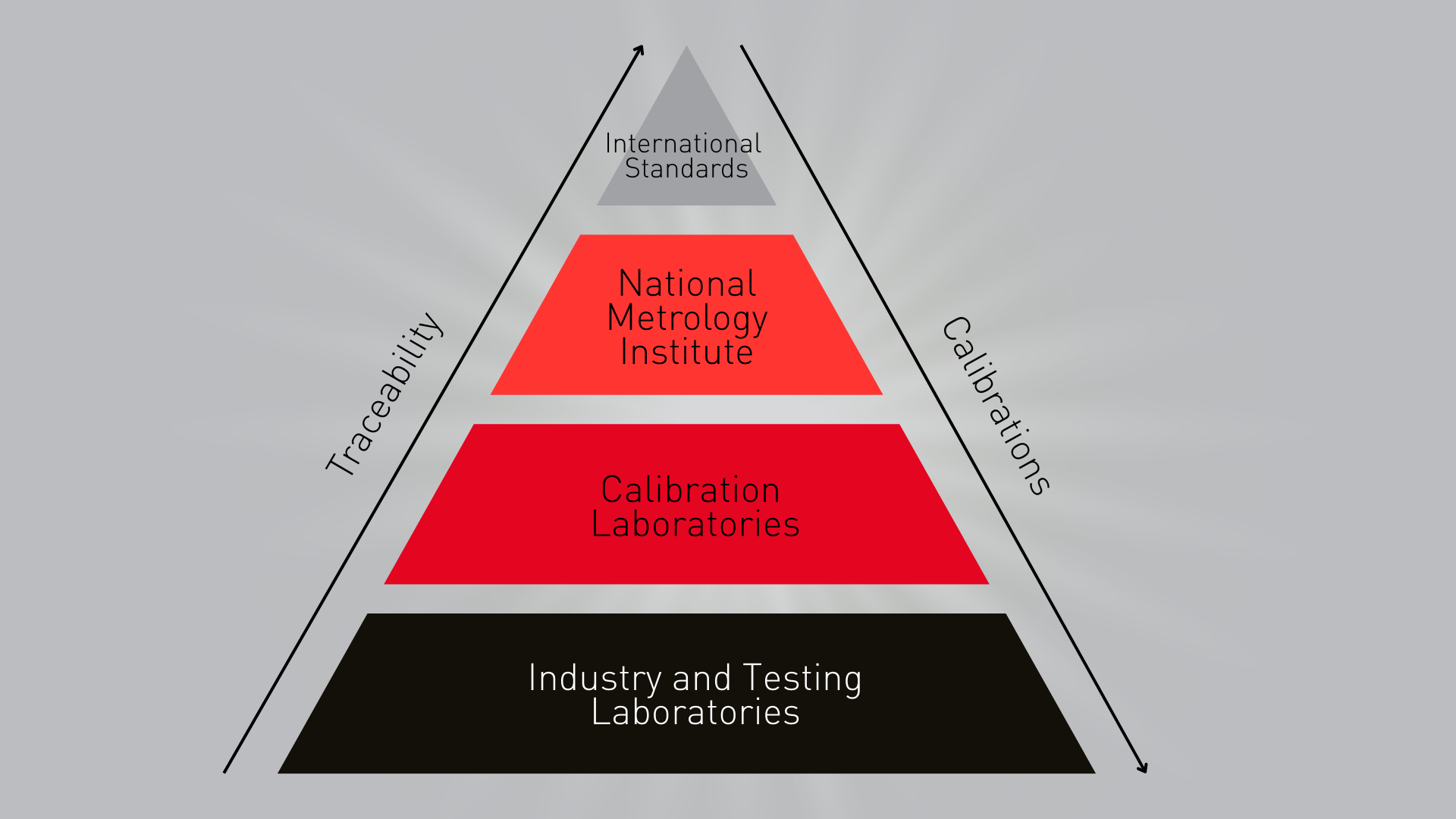
In the field of precision measurement, the metrology pyramid is a fundamental reference framework. For industrial players, understanding this structure is essential to maintaining quality, compliance, and long-term reliability. The metrology pyramid defines a hierarchical chain of traceability that links each measurement back to recognised reference standards, most notably those of the International System of Units (SI). Traceability, in this context, means that each measurement can be related to a higher-level standard through a documented chain of calibrations, each contributing to the overall uncertainty.
Reinforce Desoutter’s commitment to quality and offer expert consultation for compliance!
Discover Desoutter service


